Thursday, December 25, 2008
Abstract List
Information Retrieval Group :
1. Multi lingual text classification analysis.
2. Front end tool for transliteration
3. Data Patterns and analysis of a document class
4. Indexing of PDF document classification?
5. Canonical syllable analysis in Indic Scripts?
6. Effect of text/corpus on Telugu documents?
7. Front end for canonical syllable analyzer using TCL/TK
8. Separation of names in any Telugu document (category wise)?
9. Canonical syllable segmentation on transliterated text?
10. Extraction of common words in multi lingual text?
11.Separation nouns / verbs from text?
12.Implementation of ajax for telugu?
13.Identifying Data Patterns in a public mailing list?
14.Font creation, conversion models?
Optical Character recognition :
1. Zone separation for Indic scripts
2. Syllable segmentation in Indic Scripts?
3. Identification of plantations from images?
4. Texture Segmentation from Faces?
5. Identification a face from a picture / scene / image?
6. Classification of Indian faces from face database?
7. Gender separation from face database?
8. Octave support
a) Support for jpeg/tif images?
b) Support for image function / Image processing
Data Mining :
1. Design of CMS for data storage in a dept / college.
Friday, October 3, 2008
LabVIEW

LabVIEW (short for Laboratory Virtual Instrumentation Engineering Workbench) is a platform and development environment for a visual programming language from National Instruments. The graphical language is named "G". Originally released for the Apple Macintosh in 1986, LabVIEW is commonly used for data acquisition, instrument control, and industrial automation on a variety of platforms including Microsoft Windows, various flavors of UNIX, Linux, and Mac OS.
Virtual Instrumentation is the use of customizable software and modular measurement hardware to create user-defined measurement systems, called virtual instruments.
Traditional hardware instrumentation systems are made up of pre-defined hardware components, such as digital multimeters and oscilloscopes that are completely specific to their stimulus, analysis, or measurement function. Because of their hard-coded function, these systems are more limited in their versatility than virtual instrumentation systems. The primary difference between hardware instrumentation and virtual instrumentation is that software is used to replace a large amount of hardware. The software enables complex and expensive hardware to be replaced by already purchased computer hardware; e. g. analog to digital converter can act as a hardware complement of a virtual oscilloscope, a potentiostat enables frequency response acquisition and analysis in electrochemical impedance spectroscopy with virtual instrumentation.
The concept of a synthetic instrument is a subset of the virtual instrument concept. A synthetic instrument is a kind of virtual instrument that is purely software defined. A synthetic instrument performs a specific synthesis, analysis, or measurement function on completely generic, measurement agnostic hardware. Virtual instruments can still have measurement specific hardware, and tend to emphasize modular hardware approaches that facilitate this specificity. Hardware supporting synthetic instruments is by definition not specific to the measurement, nor is it necessarily (or usually) modular.
Leveraging commercially available technologies, such as the PC and the analog to digital converter, virtual instrumentation has grown significantly since its inception in the late 1970s. Additionally, software packages like National Instruments' LabVIEW and other graphical programming languages helped grow adoption by making it easier for non-programmers to develop systems.
Sunday, September 28, 2008
VHDL Projects
http://www.eg3.com/WebID/fpga/vhdl/blank/project/a-z.htm
http://www.itee.uq.edu.au/~peters/xsvboard/
http://www.ece.neu.edu/research/navabi/Student%20Projects.htm
http://forum.allaboutcircuits.com/showthread.php?t=3850
http://members.optushome.com.au/jekent/FPGA.htm
Thursday, July 31, 2008
Operating system support
Comparison of numerical analysis software
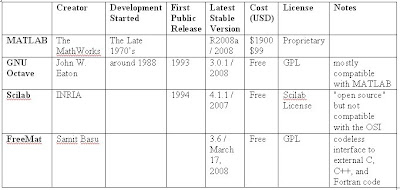
INRIA : The Institut national de recherche en informatique et en automatique
GNU : General Public License
OSI : Open Source Initiative
GNU Octave can generally run scripts written for recent versions of MATLAB; has an active user community. (free software, GNU GPL license).
Scilab is similar to MATLAB and Octave. Distributed with source (under their own license, which is not approved by the Open Source Initiative).
FreeMat, an open-source MATLAB-like environment with a GPL license.
Matlab Alternatives
 Matlab is a very powerful numerical computing environment which enables the user to perform complex mathematical and scientific function with relative ease. One of the biggest issues with Matlab is the price of it. Students can purchase an un-upgradable version for less than $100 (~£50), however this is only available for students and may only be used during the course of their studies. Commercial licenses are considerably more running into thousand of dollars/pounds depending on how many license-seats are required and what toolbox add-ons are ordered.
Matlab is a very powerful numerical computing environment which enables the user to perform complex mathematical and scientific function with relative ease. One of the biggest issues with Matlab is the price of it. Students can purchase an un-upgradable version for less than $100 (~£50), however this is only available for students and may only be used during the course of their studies. Commercial licenses are considerably more running into thousand of dollars/pounds depending on how many license-seats are required and what toolbox add-ons are ordered.There are two free alternatives that I can recommend:
 1. Octave
1. OctaveDesigned with Matlab compatibility in mind, Octave provides a simple command-line focused UI that implements many of the functions of Matlab's M-language. A lot of Matlab M-code will run directly within Octave, although there are incompatibilities,
 2. FreeMat
2. FreeMatFreeMat is a full numerical computing environment in the same mould as Matlab. It has some Matlab M-code compatibility (apparently 95% code compatibility). Actually FreeMat goes beyond the capabilities of Matlab by providing a codeless interface to other programming languages such as C, C++, and Fortran and some IDL functionality. Windows, OSX and Linux platforms are supported .
 3. Scilab
3. ScilabA third free Matlab alternative that has been recommended on the forums was Scilab. Scilab is a full numerical computing environment similar to Matlab, and although functioning with similar syntax is not fully Matlab compatible (from my initial musing less so that Octave and FreeMat). However, Scilab contains a useful Matlab > Scilab converter to port Matlab M-code into Scilab's own code. Scilab is available for Windows, UNIX and Linux.
Related Links :
FreeMat : see http://freemat.sourceforge.net/

